Working with Queries
Learn how to query your data using natural language or SQL, and understand your results effectively.
Natural Language Queries (Recommended for Beginners)
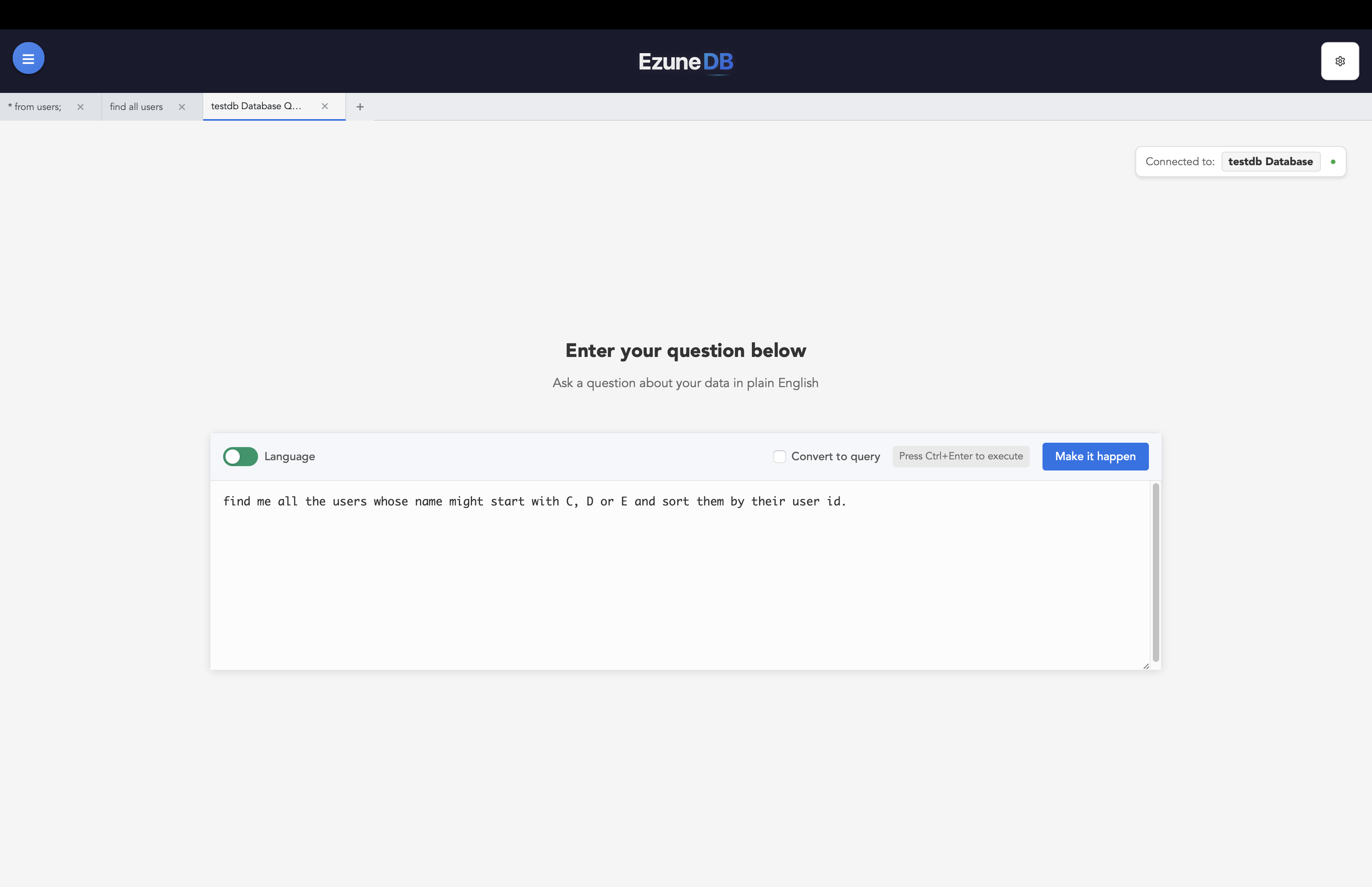
The easiest way to get started is using natural language. Simply ask questions in plain English:
Step-by-step process:
Select your database
Choose from your connected databases in the sidebar
Type your question
Ask in plain English what you want to know
Press Enter or click "Run Query"
Execute your query and see the results
Review the results
Analyze your data in the results table
Example Natural Language Queries:
"Show me all sales from last month""What are the top 10 customers by revenue?""Compare sales between 2022 and 2023""Show me products with low inventory"SQL Queries (For Advanced Users)
If you're familiar with SQL, you can write queries directly for more precise control:
How to use SQL mode:
Toggle to SQL mode
Use the switch in the query panel to enable SQL input
Write your SQL query
Use standard SQL syntax with your database's specific features
Execute the query
Click run to see your results
Example SQL Query:
SELECT customer_name, total_sales FROM sales WHERE date >= '2023-01-01' ORDER BY total_sales DESC LIMIT 10;
This query shows the top 10 customers by sales since the beginning of 2023.
Understanding Your Results
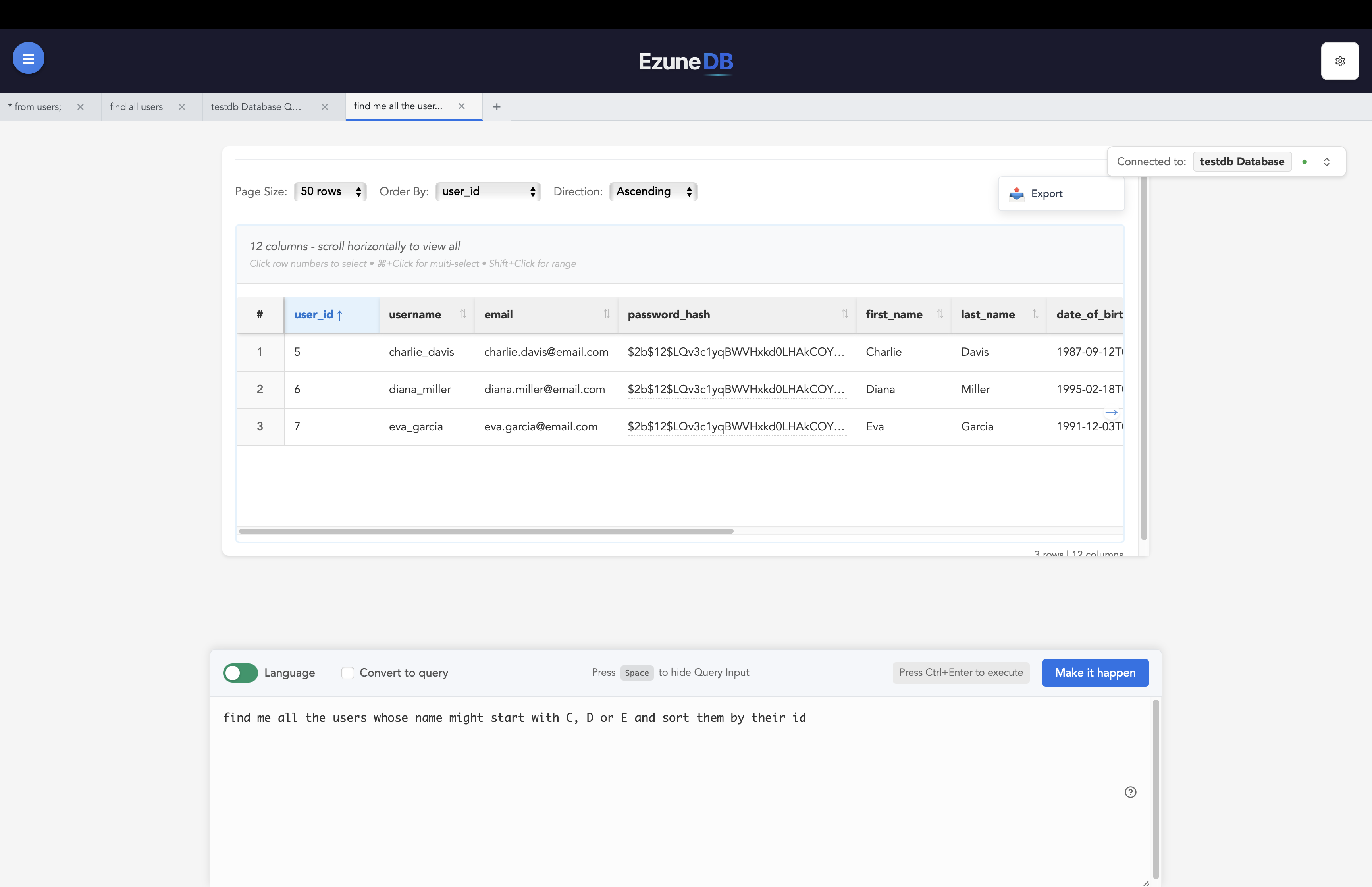
Data Table View
Table Structure
- • Rows: Each row represents one record
- • Columns: Each column shows different information
- • Headers: Click to sort data ascending/descending
Interactive Features
- • Pagination: Navigate through large datasets
- • Row Selection: Click row numbers to select
- • Sorting: Click column headers to sort
Navigation Features
Foreign Keys
Click on linked values to explore related data automatically
Go Back
Return to previous views when exploring linked data
Copy Data
Select rows and press Ctrl+C to copy to clipboard
Understanding Query Reasoning
Ever wonder what just got executed? See exactly how your natural language query gets converted to SQL with full transparency.
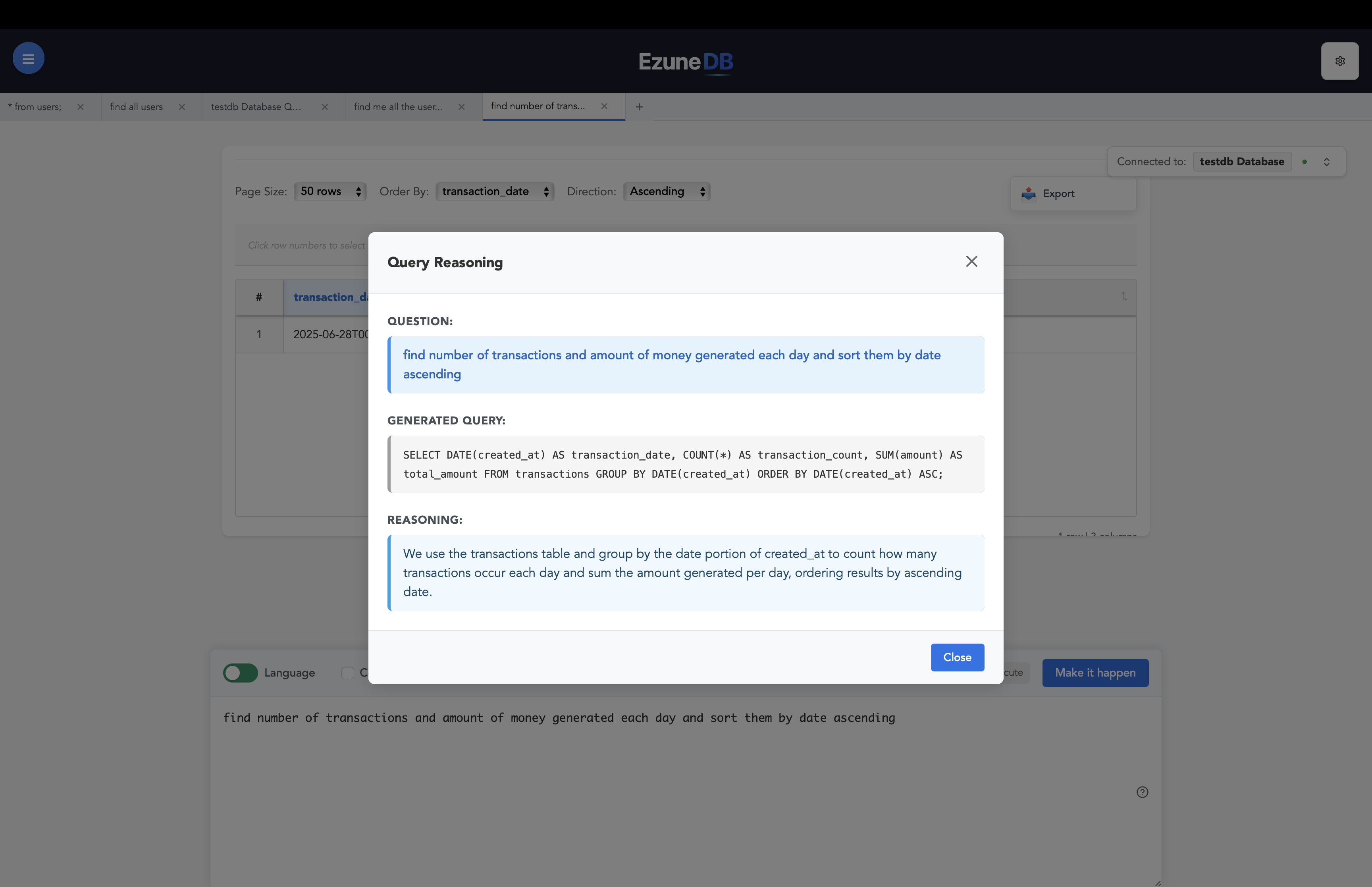
What you can see:
Query Translation
- • Your original natural language question
- • The generated SQL query
- • Which tables and columns were selected
Execution Details
- • Query execution time
- • Number of rows returned
- • Any filters or conditions applied
Best Practices for Writing Queries
Natural Language Tips
- Be specific: "Show me sales from January 2023" is better than "show me sales"
- Use time periods: "Last 30 days", "This year", "Last month"
- Include limits: "Top 10 customers" instead of "all customers"
- Use comparisons: "More than $1000", "Less than 50 units"
Performance Tips
- Filter early: Use specific date ranges and conditions
- Limit results: Start with smaller datasets to test queries
- Use indexes: Query on indexed columns when possible
- Test incrementally: Build complex queries step by step